Manage Table Schemas of Tables to be Migrated
This document describes how to manage the schema of the table in DM during migration using dmctl.
Implementation principles
When you migrate tables using DM, DM performs the following operations on the table schema:
For full export and import, DM directly exports the upstream table schema of the current time to SQL files and applies the table schema to the downstream.
For incremental replication, the whole data link contains the following table schemas, which might be the same or different:
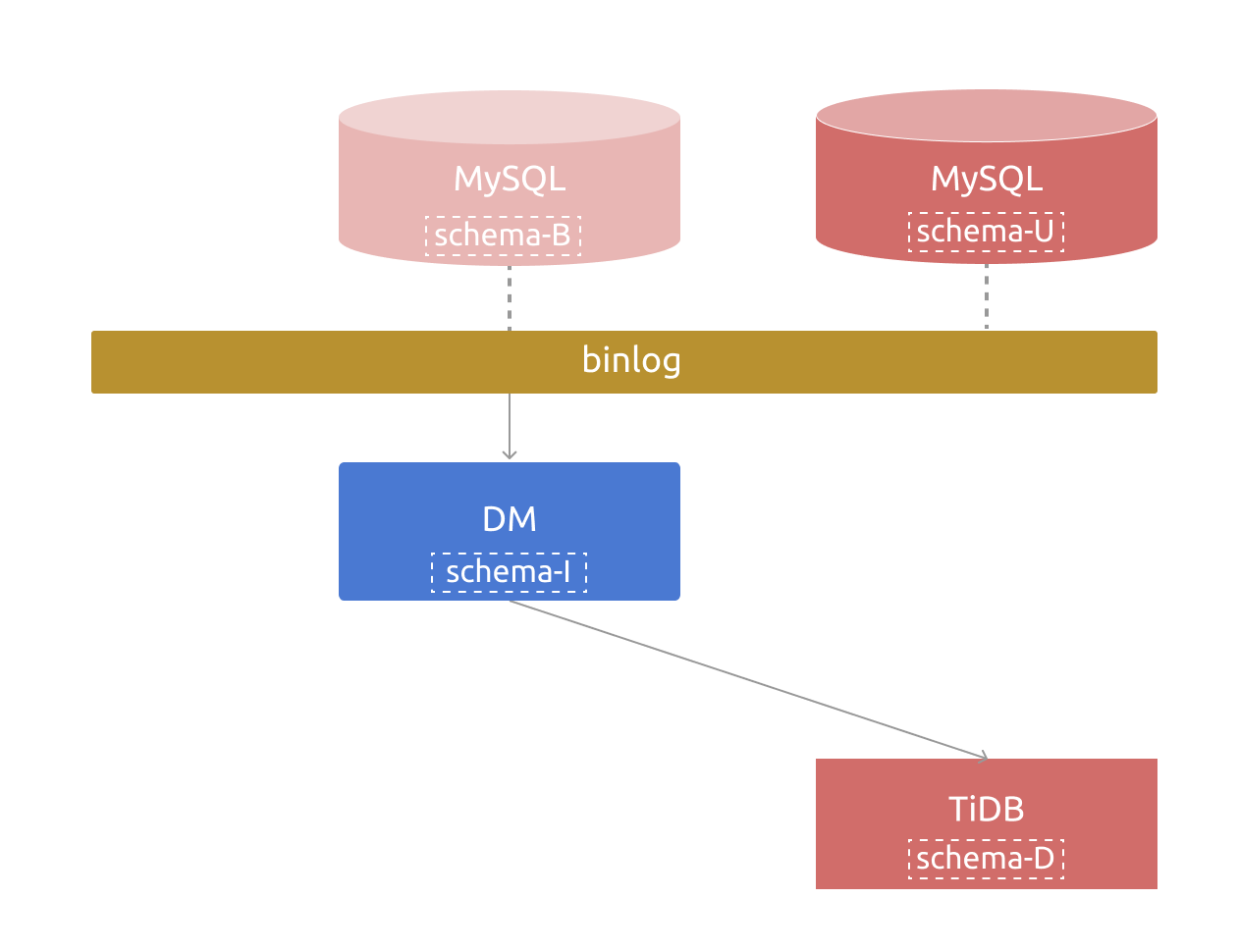
The upstream table schema at the current time, identified as
schema-U.The table schema of the binlog event currently being consumed by DM, identified as
schema-B. This schema corresponds to the upstream table schema at a historical time.The table schema currently maintained in DM (the schema tracker component), identified as
schema-I.The table schema in the downstream TiDB cluster, identified as
schema-D.In most cases, the four table schemas above are the same.
When the upstream database performs a DDL operation to change the table schema, schema-U is changed. By applying the DDL operation to the internal schema tracker component and the downstream TiDB cluster, DM updates schema-I and schema-D in an orderly manner to keep them consistent with schema-U. Therefore, DM can then normally consume the binlog event corresponding to the schema-B table schema. That is, after the DDL operation is successfully migrated, schema-U, schema-B, schema-I, and schema-D are still consistent.
However, during the migration with optimistic mode sharding DDL support enabled, the schema-D of the downstream table might be inconsistent with the schema-B and schema-I of some upstream sharded tables. In such cases, DM still keeps schema-I and schema-B consistent to ensure that the binlog event corresponding to DML can be parsed normally.
In addition, in some scenarios (such as when the downstream table has more columns than the upstream table), schema-D might be inconsistent with schema-B and schema-I.
To support the scenarios mentioned above and handle other migration interruptions caused by schema inconsistency, DM provides the binlog-schema command to obtain, modify, and delete the schema-I table schema maintained in DM.
Command
help binlog-schema
manage or show table schema in schema tracker
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema [command]
Available Commands:
delete delete table schema structure
list show table schema structure
update update tables schema structure
Flags:
-h, --help help for binlog-schema
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
Use "dmctl binlog-schema [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Parameters
delete: Deletes the table schema.list: Lists the table schema.update: Updates the table schema.-sor--source:- Required.
- Specifies the MySQL source that the operation is applied to.
Usage example
Get the table schema
To get the table schema, run the binlog-schema list command:
help binlog-schema list
show table schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema list <task-name> <database> <table> [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for list
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
If you want to get the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task, run the following command:
binlog-schema list -s mysql-replica-01 task_single db_single t1
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `c1` int(11) NOT NULL, `c2` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`c1`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_bin",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}
Update the table schema
To update the table schema, run the binlog-schema update command:
help binlog-schema update
update tables schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema update <task-name> <database> <table> [schema-file] [flags]
Flags:
--flush flush the table info and checkpoint immediately (default true)
--from-source use the schema from upstream database as the schema of the specified tables
--from-target use the schema from downstream database as the schema of the specified tables
-h, --help help for update
--sync sync the table info to master to resolve shard ddl lock, only for optimistic mode now (default true)
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
If you want to set the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task as follows:
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`c1` int(11) NOT NULL,
`c2` bigint(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`c1`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 COLLATE=latin1_bin
Save the CREATE TABLE statement above as a file (for example, db_single.t1-schema.sql), and run the following command:
operate-schema set -s mysql-replica-01 task_single -d db_single -t t1 db_single.t1-schema.sql
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}
Delete the table schema
To delete the table schema, run the binlog-schema delete command:
help binlog-schema delete
delete table schema structure
Usage:
dmctl binlog-schema delete <task-name> <database> <table> [flags]
Flags:
-h, --help help for delete
Global Flags:
-s, --source strings MySQL Source ID.
If you want to delete the table schema of the `db_single`.`t1` table corresponding to the mysql-replica-01 MySQL source in the db_single task, run the following command:
binlog-schema delete -s mysql-replica-01 task_single db_single t1
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"sources": [
{
"result": true,
"msg": "",
"source": "mysql-replica-01",
"worker": "127.0.0.1:8262"
}
]
}